Naipu NP-IS Series are single-stage single suction horizontal end suction centrifugal pumps designed for clean water or similar liquids in water supply and drainage applications in municipal, industrial and agricultural irrigation projects.
Typical Applications---
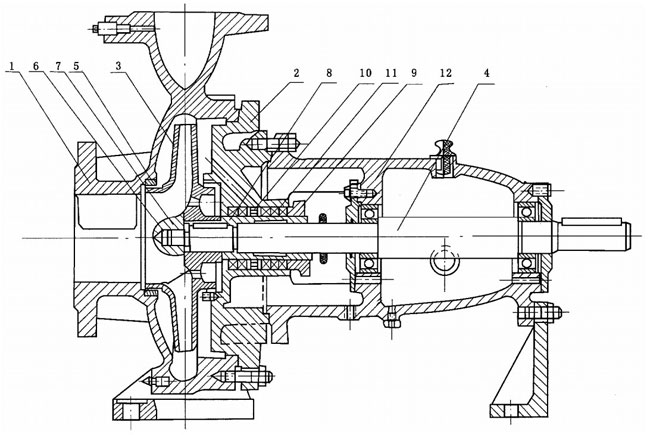
Construction Drawing
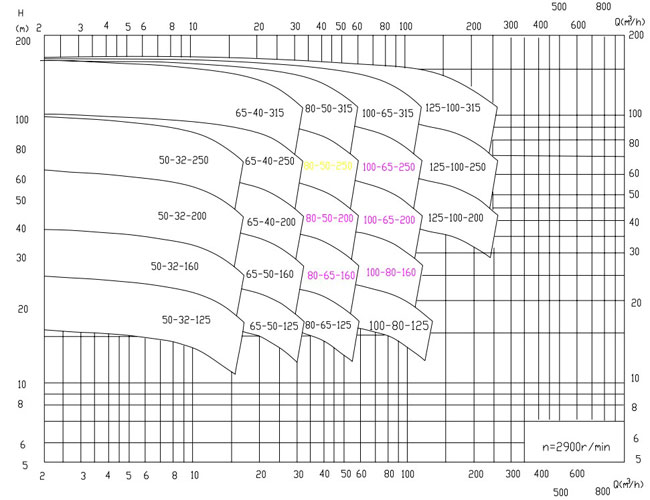
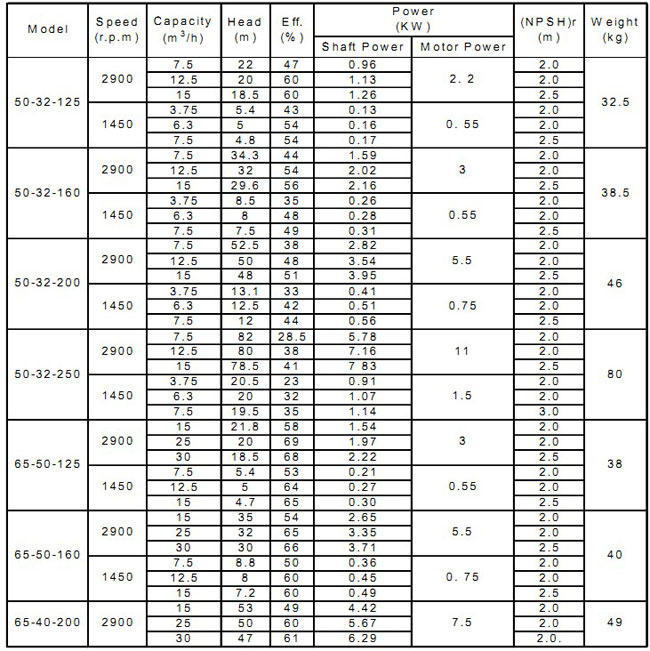
NP-IS Water Pump Selection Sheet
NP-IS WATER PUMP PERFORMANCE PARAMETERS
IS Clean Water Pump,Single Stage Water Pump,Centrifugal Clean Water Pump Shijiazhuang Naipu Pump Co., Ltd. , https://www.naipu-pump.com

Tank filling
Water supply
Water transfer
Pressure boosting
Irrigation
A overview
Copper-nickel sulfide ores, the nickel-containing minerals pyrite nickel, needle sulfur nickel ore, nickel ore red, nickel-containing pyrrhotite.
The flotation of nickel minerals is required to be carried out in acidic, neutral or weakly alkaline media. The collector uses a high-grade xanthate such as diced yellow or medicinal medicinal herbs. Nickel-containing pyrrhotite is more difficult to float than other nickel minerals. The best flotation medium is weakly acidic or acidic, and the flotation rate is very slow. In the alkaline medium caused by lime, the above nickel minerals can be inhibited, but the degree of inhibition is different. The most easily inhibited is nickel-containing pyrrhotite. For example, when PH=8.2~8.5, the needle sulfur nickel ore can still be Floating, while nickel-containing pyrrhotite is inhibited.
Copper minerals in copper-nickel ore, typically chalcopyrite. Copper-nickel ore frequently contains a noble metal, such as platinum, the other, the recovery should be noted.
B. Characteristics of flotation of copper-nickel ore
The selection of copper-nickel ore flotation schemes should mainly consider factors such as the floatability of minerals; the symbiotic relationship of minerals; the oxidation and mud formation of nickel minerals; the types of gangue minerals. The choices are as follows:
(1) Flotation properties of copper and nickel minerals. The flotation speeds of copper minerals and nickel minerals vary greatly, as shown in Figure 1. Copper minerals float faster and nickel minerals are slower. Production practice has proved that when copper-nickel ore is flotation, about 90% of the chalcopyrite can be floated in the first 5 minutes. The floating speed of nickel minerals is slow, especially for nickel-bearing pyrrhotite, which usually takes 20~30 minutes to float. The difference in the flotation rate of copper-nickel minerals has been used in the practice of copper-nickel preferential flotation, and the "fast" flotation of copper is carried out when copper is preferentially floated. The process is characterized by increasing the speed at which the slurry passes through the flotation machine, the collector is treated with a low-grade xanthate, and is administered in a "starvation" manner. The copper flotation tailings plus copper sulfate activates the nickel minerals, and then the higher xanthate, such as the diced yellow and the medicinal yellow minerals.
Figure 1 Chalcopyrite and nickel minerals during copper-nickel ore flotation
Flotation speed of (nickel pyrite, nickel-containing pyrrhotite)
(2) The form of nickel minerals in the ore. Nickel minerals rarely form separate aggregates, mostly dispersed in other sulfide minerals, mainly pyrrhotite and chalcopyrite. Nickel is also often present in other sulfide minerals in the form of isomorphous impurities, especially in conjunction with pyrrhotite, nickel minerals, copper sulfide, and iron minerals. This brings two problems: one is nickel fine. The content of ore nickel is relatively low, generally containing Ni 3% to 5%, and the lowest limit is 2% to 2.5%. Therefore, if the ore contains Ni> 2%. It can be directly smelted; the second problem is the impact of copper-nickel separation. Copper-nickel minerals are closely symbiotic, and even if they are very fine, they cannot be dissociated from each other. Only copper-nickel mixed concentrates are obtained. After smelting, copper-nickel separation is carried out. If the nickel-containing minerals are only closely related to the pyrrhotite and the relationship with the chalcopyrite is relatively simple, it is possible to obtain a copper concentrate and obtain a so-called iron-nickel concentrate having a lower nickel content.
(3) Oxidation and muddy of nickel-containing minerals. Nickel-containing minerals such as nickel pyrite and nickel-bearing pyrrhotite are not only easily oxidized, but also easily muddy. Therefore, when the vulcanized mineral in the ore is unevenly embedded, the stage grinding process is particularly important. Generally, under the condition of coarse grinding, copper-nickel mixed flotation is carried out to obtain waste tailings. The mixed concentrate is re-classified and then subjected to selective or copper-nickel separation. It is important to strengthen the grading before and after the regrind operation.
In order to eliminate the interference of a nickel-containing pyrrhotite, Canadian Forest Lake beneficiation plant, using a magnetic nickel pyrrhotite, rear (65% -0.074mm) coarse grinding, with 15% of the selected magnetic separator magnetic products, After selection, it is used as a nickel concentrate. After the non-magnetic portion is reground, copper-nickel mixed flotation is performed. [next]
In order to improve the floatability of the non-floating nickel sulfide ore, the plant used SO 2 gas in the non-magnetic part of copper-nickel mixed flotation. The original slurry has a natural pH of 8.8, and after treatment with SO 2 gas, the pH drops to 5.6. After treatment with SO 2 gas, the floatability of the nickel sulfide mineral is improved.
(4) The influence of gangue minerals. Copper-nickel ore often contains some buoyant gangue, such as chlorite, sericite, serpentine and talc. They are easy to muddy and the slime is easy to float. Into the concentrate containing magnesium sludge, not only reduces quality, but also affect the smelting. It is generally required that the nickel concentrate contains not more than 5% to 9% of magnesium oxide.
There are two ways to eliminate the easy-flowing gangue slime: the first is to add a small amount of foaming agent to pre-float. This method is not always effective, especially in the case of backwater, because the backwater contains collector, it will increase the loss of copper and nickel in the slime; the second method is to use inhibitors such as water glass, dextrin and carboxy Methyl cellulose, etc.
C copper-nickel separation
There are two major types of flotation schemes for copper-nickel ore; one is preferential flotation; the other is mixed flotation. In the case where the copper content in the ore is higher than that of nickel and the mineral symbiosis relationship is relatively simple, preferential flotation can be considered. The advantage is that copper concentrate and nickel concentrate can be directly obtained; the disadvantage is that the nickel mineral which is suppressed when floating copper is not easy to be activated, and the recovery rate of nickel is low, so this method is rarely used.
Copper-nickel mixed flotation is currently a more general solution. The advantage is that the recovery rate of nickel is higher than that of the preferred flotation, and the flotation equipment is also preferred for flotation. Copper-nickel mixed flotation is similar to copper-sulfur mixed flotation. For the ore containing more nickel magnetite in the ore, there are two treatment schemes; one is to use magnetic separation to separate a part of nickel-containing pyrrhotite and then to float; the other scheme is First, float the chalcopyrite and nickel pyrite, and then float the nickel pyrrhotite. When nickel-containing pyrrhotite is floated, it can be activated by copper sulfate. For some refractory nickel sulfide ore with strong alteration, the pulp is treated with gas to reduce the PH value to about 5-6, which has proved to be effective. The separation of copper-nickel mixed concentrates is all nickel-free float copper. The main methods are listed in Table 1.
Table 1 Main methods of copper and nickel separation
Method name
Typical concentrator
Lime + dextrin method
Lime + hydride method
Lime + steam heating
Finland's Tolanti
Forest Lake, Canada
Former Soviet Rilsk
Among the copper-nickel ore that is processed by the Tolanti concentrator in Finland, the main nickel-bearing ore is nickel pyrite and nickel-containing magnetite. Copper minerals are chalcopyrite. Gangue minerals amphibole, plagioclase, mica and quartz. The process of the plant is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Finland Folland copper-nickel ore flotation process [next]
In the copper-nickel mixed flotation, adjust the pH and inhibit the silicate gangue with sulfuric acid (6.4 kg/t), the xanthate (60 g/t) as the collector, and the coarse pine oil (290 g/t). Foaming agent. When separating copper and nickel, use lime (1kg/t) plus dextrin (25 g/t) to suppress nickel minerals. The main feature of the process is that the inhibition of nickel minerals, according to the difference in floatability, is carried out according to the mineral component, that is, the nickel-bearing pyrite is first suppressed, and the nickel pyrite is further suppressed. The indicators obtained are as follows:
grade/%
Recovery rate/%
Cu
Ni
Cu
Ni
Nickel concentrate
Copper concentrate
Tailings
Raw ore
0.7
29.26
0.04
0.26
5.84
1.19
0.042
0.69
29.8
62.3
7.9
100
93.6
1.0
5.4
100
Due to the complex mineral composition, it is difficult to separate the copper-nickel mixed concentrate by the general method. In recent years, research and practice have proved that it is more effective to use lime + steam heating method. The former Soviet Union Norilsk beneficiation, at the same time processing the dip mine and vein ore two ore, due to the complex mineral composition, various mineral forms, the same mineral has several kinds of crystal deformation, so the separation of copper and nickel mixed concentrate with lime, sulfite Both the thiosulfate and the thiosulfate did not give satisfactory results.
The wide use of lime + steam heating method, while adding lime, steam is introduced. The temperature of the slurry accelerates the desorption of the collector from the surface of the nickel mineral and the pyrrhotite, and forms a relatively stable oxide film on the surface of these minerals to enhance their inhibition. For the amount of lime, for the impregnated ore, the free CaO content in the slurry is required to be 600-800 g/m 3 ; the vein ore is 200-300 g/m 3 . When the steam is warmed, the slurry temperature is 70 ° C, the heating time is 12-15 min, and the pulp concentration is 40% solid. After the slurry is warmed, it is diluted to about 32% solids for "fast" flotation of copper, and the tailings are nickel concentrate. The foam product is graded and ground to float copper to obtain copper concentrate, and the tailings are nickel concentrate.